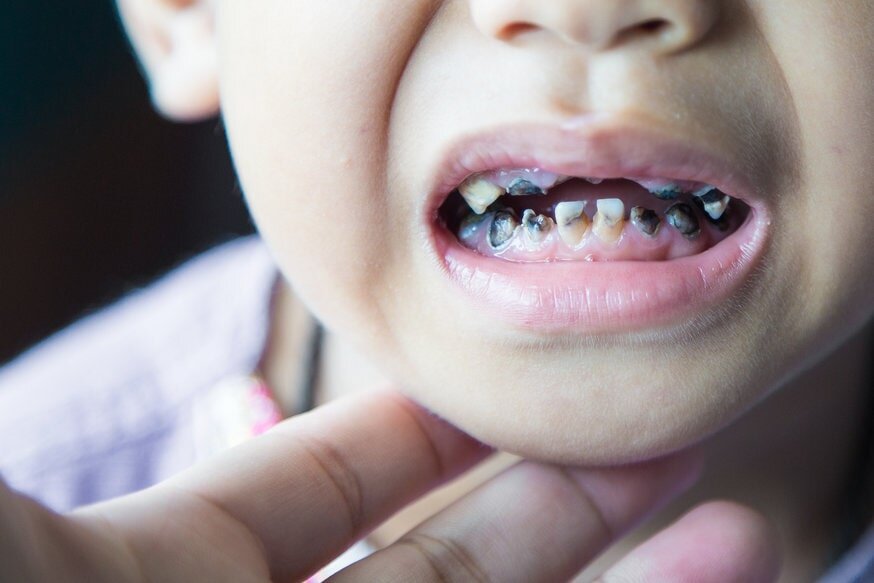
Cavity Concerns: Addressing Tooth Decay in Children
Tooth decay is one of the most prevalent dental problems worldwide. It is the breakdown, or destruction of the outer enamel layer, leading to tiny holes or pits. Kids are more susceptible to developing tooth decay because primary teeth have a thinner, softer enamel (the outer hard mineral layer of the tooth), and kids have poor oral hygiene and unhealthy eating habits.
Read the article further to learn more about the causes of tooth decay in kids, the risk factors, and the effective preventive measures offered by the dentist in Plymouth, MN.
| Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, is the destruction of the tooth surface due to the breakdown of the enamel layer. Increased bacterial accumulation leads to the formation of plaque (soft sticky film covering the tooth surface) that produces harmful acids, toxins, and by-products. These toxins demineralise the hard layer of the tooth forming tiny holes, pits, or cavities. If left untreated, tooth decay in kids can cause pain, swelling, infection, and even tooth loss. |
Etiology
The oral cavity (mouth) is filled with bacteria which is harmful since it combines with food to form a soft, sticky, gelatinous film called plaque. Poor oral hygiene practices can aggravate bacterial and plaque accumulation. The bacteria and plaque together use the sugar and starch from the foods one eats and drinks to produce acids and toxins. These by-products erode the hard mineral layer on the enamel and develop cavities. Over a while, the plaque can harden to form calculus (tartar), which not only damages the teeth but also irritates the gums to cause gum disease
Clinical features
The common signs and symptoms based on the different stages of tooth decay include-
- Initially, white spots appear to form on the teeth in the affected areas. This may lead to early tooth sensitivity to hot, and cold, foods
- A pit or tiny hole (cavity) may begin in the affected area. This may appear yellow, or light brown
- The gums around the affected tooth may be red and swollen
- The cavity may enlarge and widen, spreading into the deeper areas of the tooth.
- Tooth discoloration
- Pain and discomfort
- Increased tooth sensitivity to hot and cold foods
- Halitosis (bad breath)
- Increased gingival swelling, redness, and bleeding
Treatment
Some common treatment options based on the extent of tooth decay and severity of symptoms include:
- Fluoride treatment
- Dental fillings
- Root canal
- Pulpotomy
- Pulpectomy
- Tooth extraction
Tooth decay is common in children which is attributed to poor oral hygiene and unhealthy eating habits. If you notice any discoloration or cavities in your kid’s teeth consult a dentist right away for further assessment and management.
